ESSENTIALS AND APPLICATIONS OF MATHEMATICAL AND PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL SCIENCE
B.sc COMPUTERS-2
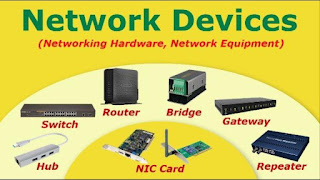
1. Explain different types of Networks?
Network allows different computers to connect and communicate with each other through a medium. Major types of network mediums are LAN, MAN and WAN. Users will select anyone of the medium depending on the area of network they want to cover. One of the major differences between them is the geographical area they cover.
1. Local Area Network:
It is also known as LAN. It is mainly designed for small physical area covered organization. LAN is a simple network. It is just the inter connection of at least two computers. For sharing files and network in between them. While if the connection is for entire building then it will become a complex problem.
Characteristics of LAN:
1. LAN is a private network. It is not subject to any traffics or any other regulatory controls.
2. When compared to the WAN, LAN’s will operate at relatively high speed.
Applications of LAN:
1. In LAN we can make one computer as a server which serves all the remaining computers commonly known as clients.
2. By using LANs we can share common resources like printers etc.
3. Main advantage of LAN is easy to design and to troubleshoot.
2. Metropolitan Area Networks:
It is also known as MAN and uses the same technology as LAN. It is developed to extend its coverage over the entire city. It can be the connection of number of LAN’s into a larger network or simply it can be a single cable. It is mainly handle and operated by single private company.It may be the connection between two or more computers which are apart but exist in the same or different cities. MAN is mainly designed for those customers who need high speed internet connectivity.
Characteristics of MAN:
1. MAN generally covers towns and cities(50 km)
2. The communication medium used for Metropolitan Area Network are cables, optical fibres etc.
Applications of MAN:
1. Main advantage of using MAN is it provides efficient and fast communication through high- speed medium, such as fibre optic cables.
2. It acts as a back bone for larger networks and provides a greater access to WAN’s.
3. In MAN for transmission of data they use dual bus which is used to transmit the data in both the directions at the same time.
3. Wide Area Network:
It is also known as WAN. It can be private or may be public leased network. it we want to share the network throughout the country or any larger geographical area then this WAN is used . the data rate in WAN is slow about a 10th of LAN’s speed because it involves greater distance and many number of servers and terminals etc.
Characteristics of WAN:
1. Generally WAN covers greater distances (like states, countries, and continents).
2. In WAN we use satellite , public telephone networks as communication medium which are linked by routers.
1. One of the main advantages is instant messaging to anyone in the network.
2. These messages include images, audio.
3. Costly things (like printers or phone lines to the internet) can be commonly shared by all the computers connected in the network.
1.
PAN(Personal Area Network):
v Personal Area Network is a network arranged within an individual person, typically within a range of 10 meters.
v Personal Area Network is used for connecting the computer devices of personal use is known as Personal Area Network.
v Thomas Zimmerman was the first research scientist to bring the idea of the Personal Area Network.
v Personal Area Network covers an area of 30 feet.
v
Personal computer devices that are used to develop
the personal area network are the laptop,
mobile phones, media player and play stations.
2. CRYPTOGRAPHY
Cryptography is the process of hiding or coding information so that only the person a message was intended for can read it. The art of cryptography has been used to code messages for thousands of years and continues to be used in bank cards, computer passwords, and ecommerce.
Why is cryptography important?
Cryptography is an essential cybersecurity tool. Its use means that data and users have an additional layer of security that ensures privacy and confidentiality and helps keep data from being stolen by cybercriminals. In practice, cryptography has many applications:
· Confidentiality: Only the intended recipient can access and read the information, so conversations and data remain private.
· Integrity of data: Cryptography ensures that the encoded data cannot be modified or tampered with enroute from the sender to the receiver without leaving traceable marks— an example of this is digital signatures.
· Authentication: Identities and destinations (or origins) are verified.
· Non-repudiation: Senders become accountable for their messages since they cannot later deny that the message was transmitted—digital signatures and email tracking are examples of this.
In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding information. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Ideally, only authorized parties can decipher a ciphertext back to plaintext and access the original information.
Decryption
Decryptionis a process that transforms encrypted in
formation into its original format. The process of encryption transforms information from its original format — called plaintext — into an unreadable format — called ciphertext — while it is being shared or transmitted.
In cryptography, plaintext is usually ordinary readable text before it is encrypted into ciphertext, or readable text after it is decrypted.
keys:
Public-key cryptography, or asymmetric cryptography, is the field of cryptographic systems that use pairs of related keys. Each key pair consists of a public key and a corresponding private key. Key pairs are generated with cryptographic algorithms based on mathematical problems termed one-way functions.
3. What is firewall?
Nowadays, it is a big challenge to protect our
sensitive data from unwanted and unauthorized sources. There are various tools
and devices that can provide different security levels and help keep our
private data secure. One such tool is a 'firewall' that prevents unauthorized
access and keeps our computers and data safe and secure.
What is a Firewall?
A firewall can be defined as a special type of network security device or a
software program that monitors and filters incoming and outgoing network
traffic based on a defined set of security rules. It acts as a barrier between
internal private networks and external sources (such as the public Internet).
The primary purpose of a firewall is to allow non-threatening traffic and
prevent malicious or unwanted data traffic for protecting the computer from
viruses and attacks. A firewall is a cybersecurity tool that filters network
traffic and helps users block malicious software from accessing the Internet in
infected computers.
Brief History of Firewall
Firewalls have been the first
and most reliable component of defense in network security for over 30 years.
Firewalls first came into existence in the late 1980s. They were initially
designed as packet filters. These packet filters were nothing but a setup of
networks between computers. The primary function of these packet filtering
firewalls was to check for packets or bytes transferred between different
computers.
Firewalls have become more
advanced due to continuous development, although such packet filtering
firewalls are still in use in legacy systems.
As the technology emerged, Gil
Shwed from Check Point
Technologies introduced the first stateful inspection
firewall in 1993. It was named as FireWall-1. Back in 2000, Netscreen came
up with its purpose-built firewall 'Appliance'.
It gained popularity and fast adoption within enterprises because of increased
internet speed, less latency, and high throughput at a lower cost.
How does a firewall work?
A firewall system analyzes
network traffic based on pre-defined rules. It then filters the traffic and
prevents any such traffic coming from unreliable or suspicious sources. It only
allows incoming traffic that is configured to accept.
Functions of Firewall
Firewalls have become so powerful, and include a
variety of functions and capabilities with built-in features:
- Network Threat Prevention
- Application and Identity-Based Control
- Hybrid Cloud Support
- Scalable Performance
- Network Traffic Management and Control
- Access Validation
- Record and Report on Events
Limitations of Firewall
When it comes to network
security, firewalls are considered the first line of defense. But the question
is whether these firewalls are strong enough to make our devices safe from
cyber-attacks. The answer may be "no". The best practice is to use a
firewall system when using the Internet. However, it is important to use other
defense systems to help protect the network and data stored on the computer.
Because cyber threats are continually evolving, a firewall should not be the
only consideration for protecting the home network.
- Firewalls cannot stop users from accessing
malicious websites, making it vulnerable to internal threats or attacks.
- Firewalls cannot protect against the transfer
of virus-infected files or software.
- Firewalls cannot prevent misuse of passwords.
- Firewalls cannot protect if security rules are
misconfigured.
- Firewalls cannot protect against non-technical
security risks, such as social engineering.
- Firewalls cannot stop or prevent attackers
with modems from dialing in to or out of the internal network.
- Firewalls cannot secure the system which is
already infected.
4.Explain about DNS?
A. The World Wide
Web that we know today would have not existed, if it was not for the Domain Name System. Every day when you go
online and open a website, the Domain Name
System is the backend, which helps you see the website you want. Domain
Name System and represents a powerful Internet
technology for converting domain names to IP
addresses. Its
special mission
is to be a mediator between the IP addresses, the system-side names of the websites
and their respective domains, and their user-side alphanumeric titles. Another important
function of the DNS is to
control the delivery of email messages Behind every site,
there is an IP address. But, while it's easy to remember the name of a website, it's quite hard to remember the exact IP address.
How does it work?
When a user wants to visit Computer Hope, they can type
"https://www.computerhope.com" into the address bar of their browser. Once that domain name has been
entered, it is looked up on a
Domain Name System where it is translated into an IP address that is more
easily interpreted by a computer,
e.g. 45.79.151.23. Using that IP address, your computer can then
locate the Computer Hope web page and forward that information to your browser.
Below is a visual example of how DNS works.
As seen above, not every DNS stores every address on the Internet.
If a domain name is not found,
the server may query other domain servers to obtain its address.
Domain name services and applications are software
programs or platforms that utilize domain names to provide various
functionalities. Here are some examples of domain name services and
applications:
1. Website Builders: Website builders like Wix, Squarespace, and Weebly allow users to create and publish websites using a custom domain name. These platforms provide templates, design tools, and features to create a website without needing to know how to code.
2. Domain Name Registrars: Domain name registrars like
GoDaddy, Namecheap, and Google Domains allow users to register and manage
domain names. They provide tools to configure DNS settings, set up email
accounts, and manage domain name renewal and transfer.
3. DNS Management Tools: DNS management tools like
Cloudflare, DNSimple, and Amazon Route 53 provide a way to manage DNS records
and settings for a domain name. These tools allow users to configure DNS
settings, set up subdomains, and monitor DNS traffic.
4. Email Services: Email services like G Suite,
Microsoft 365, and Zoho Workplace allow users to create email accounts using a
custom domain name. These services provide email hosting, calendar, and
collaboration tools for businesses and individuals.
5. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs like
ExpressVPN, NordVPN, and TunnelBear allow users to secure their internet
connection and protect their online privacy. Some VPNs provide the option to
use a custom domain name for their VPN server.
6. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs like
Cloudflare, Akamai, and Fastly provide a network of servers that cache and
deliver content from a website or application. Some CDNs allow users to set up
a custom domain name for their CDN endpoint.
7. Load Balancers: Load balancers like NGINX, HAProxy, and Amazon Elastic Load Balancer distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers to improve the performance and scalability of a website or application. Some load balancers allow users to set up a custom domain name for their load balancer.
5.Explain Milestones of Computer Evolution?
DEFINITION
A computer is an electronic
machine that takes input from the user, processes the given input and generates
output in the form of useful information.
Explain Characteristics
of computers.
Speed: Computer is fast
working device. A computer has the ability to process large volume of data and
to retrieve the data in a fraction of seconds. It can perform one billion
instructions per seconds.
Units of speed
Micro seconds----10-6
Nano seconds-------10-9
Pico
seconds-------------10-12
Accuracy: Computer is a very
accurate device or even it can be called 100% accurate device. It never gives a
wrong result until we give the incorrect input data.
Eg: divide by zero
Automatic: A machine which
works itself without any human participation is said to be an automatic
machine. A set of instructions which acts as a program code are given to
computer and it processes these instructions automatically.
Storage:
Computer can store and recall any amount of information. Data will be stored in
the form of binary code (0, 1) alternatively called as bits.
Diligence:
The computer can work continuously without getting tired and lack of
concentration.
Versatility:
Computer is a machine which can solve different problems like preparing charts,
electricity bills
Data Base:
The use of computer facility in business organisation helps in establishment of
database. Data base integrates data records and reduces data redundancy.
Limitations of Computer Systems
Lack of common-sense:
This is one of the major limitations
of computer systems. No matter how efficient, fast and reliable computer
systems might be but yet do not have any common sense. As computers function
based on the stored programme(s), they simply lack common sense.
Zero IQ
Another of the limitations of computer systems is that they have zero Intelligence Quotient (IQ). They are unable to see and think the actions to perform in a particular situation unless that situation is already programmed into them. Computers are programmable to complete each and every task, however small it may be.
What is the history of computers?
In
olden days man used to count things with the help of stones slowly they came to
use their fingers for counting. But to count fast and to calculate through a
machine .Then they started inventing machines to calculate .Essentially there
are three types of calculating devices:
1.
manual devices
2.
mechanical devices
3.
automatic devices
v Abacus: It was the first
manual calculating machine .It was invented by Chinese in 3000BC.It is used for
calculating addition, subtraction. The
shape of the machine is rectangular box looks like beads on a rack
v Napier’s Bones: It was invented
by “JOHN NAPIER” in 1960. It is used to multiplications and divisions.
v Pascaline:
It was invented by ”BLAISE PASCAL “in
1642.It was the first mechanical calculator used for addition, subtractions, multiplications
and divisions. Multiplications and divisions were done as series of additions
and subtractions respectively.
v Arithmetic Replica:
It was invented by “BARON
GOTTFRIED LEIBENIZ” (Germany) in 1673.It was used to solve all arithmetic
problems.
v Differential And
Analytical Engine: Both are developed by “CHARLES BABBAGE
“in 1822.The first lady computer programmer is”ADAAUGUSTA LOVELACE” (Daughter
of famous British poet lard Byron).She was appointed as programmer for
developing software by Charles Babbage.
v Punched Card Reading
Machine: It
was developed by “Herman Hollerith” in 1890.
v Mark-1: It was the first electro mechanical
computer. It is invented by “HOWARD EIKENS” from Harward University for IBM Company
in 1937.It used punched card concept for input and output. This was the first
fully automatic calculating machine.













Comments
Post a Comment